22-year-old female presents to the Urgent Care Clinic with a “fast heart rate” and palpitations. She has experienced this before, but she came today because the current episode is lasting longer than usual. She is slightly dizzy but otherwise asymptomatic. She is in no apparent distress, is breathing comfortably, and has 2+ peripheral pulses. Her vitals are within normal limits except a heart rate of 162. Her ECG is shown below:

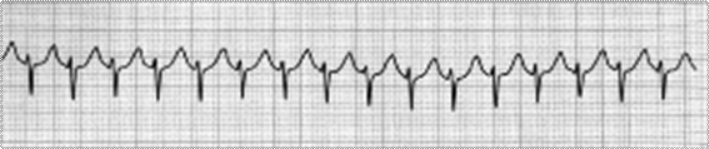
1. What would be your initial management of this patient?
2. Vagal maneuvers effectively achieve cardioversion in approximately 28% of patients [5]. However, the efficacy drastically increases when using the “modified Valsalva” technique described in the REVERT trial.
In order to complete the maneuver:
3. If vagal manoeuvres fail, what is your next course of action?
4. With regards to the use of Adenosine, which of the following statements is INCORRECT ?



